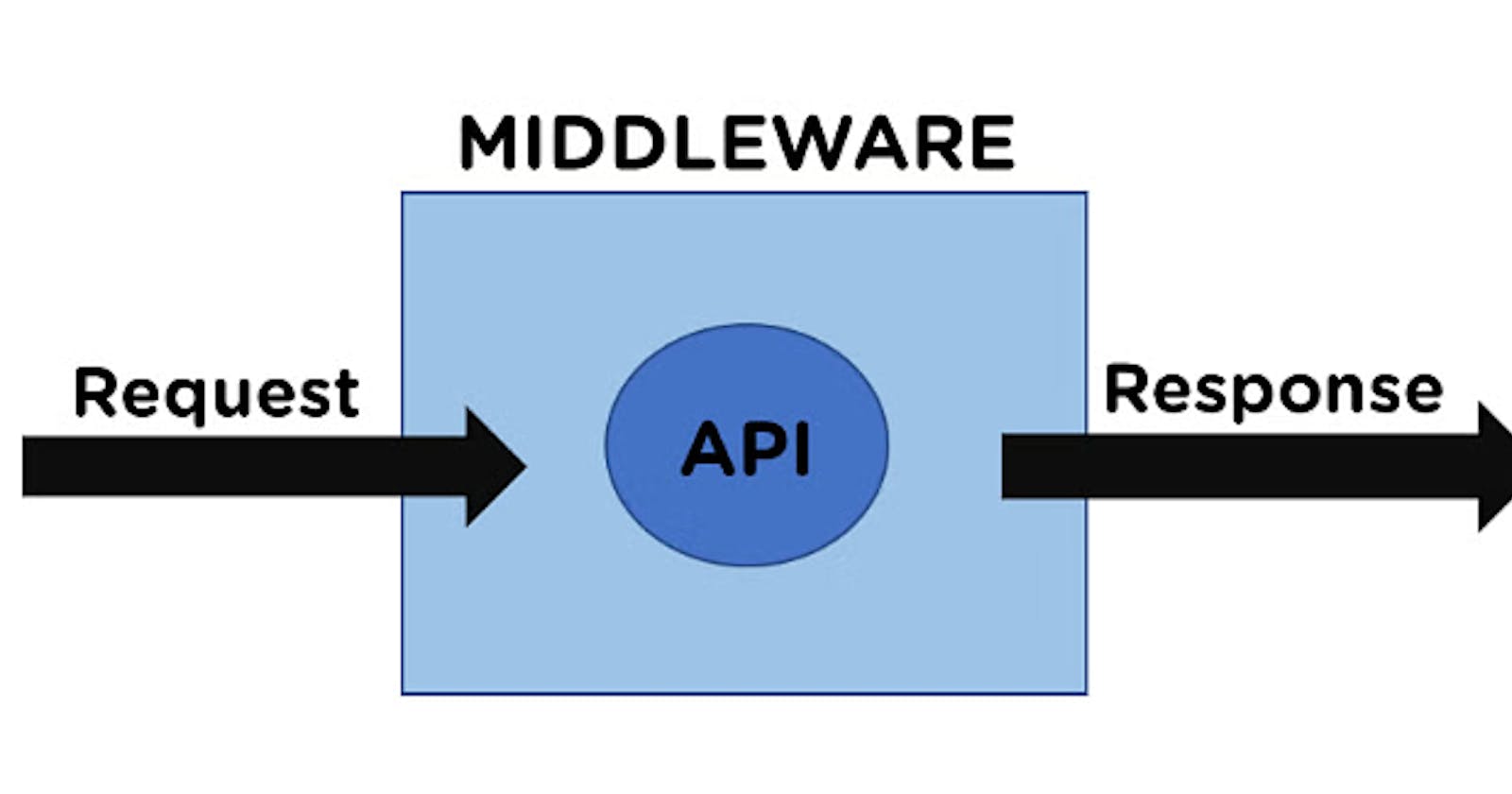
What Is Middleware?
In simple terms, middleware in Express is like a relay race: it receives an incoming request, performs some actions, and then passes control to the next middleware or route handler. It sits between the request and response cycle, allowing you to add functionality, modify data, or perform checks.
Types of Middleware
Application-Level Middleware:
Bound to the entire Express application using
app.use()or specific HTTP methods (app.get(),app.post(), etc.).Executes for every incoming request.
Example:JavaScript
const express = require('express'); const app = express(); // Log timestamp for every request app.use((req, res, next) => { console.log('Time:', Date.now()); next(); });
Router-Level Middleware:
Associated with specific routes using
router.use()or HTTP methods within a router.Executes only for requests matching the specified route.
Example:JavaScript
const express = require('express'); const router = express.Router(); // Log request type for /user/:id route router.use('/user/:id', (req, res, next) => { console.log('Request Type:', req.method); next(); });
Error-Handling Middleware:
Handles errors during request processing.
Defined with four parameters (err, req, res, next).
Example:JavaScript
app.use((err, req, res, next) => { console.error(err.stack); res.status(500).send('Something broke!'); });
Built-In Middleware:
Included with Express (e.g.,
express.json(),express.urlencoded()).Parses request bodies, handles static files, etc.
Third-Party Middleware:
External packages (e.g.,
morgan,helmet,cors).Enhance functionality or security.
Example: Logging Middleware
Let’s create a simple Express API with logging middleware:
Install Express:
npm install expressCreate
server.js:JavaScript
const express = require('express'); const app = express(); // Application-level middleware app.use((req, res, next) => { console.log('Request URL:', req.originalUrl); next(); }); // Route handler app.get('/user/:id', (req, res, next) => { console.log('User ID:', req.params.id); res.send('User Info'); }); const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000; app.listen(PORT, () => { console.log(`Server running on port ${PORT}`); });Run the server:
node server.js
Now you have a basic understanding of Express middleware! Feel free to explore more middleware options and build powerful applications. 🚀